|
The
table below describes how to create a new BufferPrep recipe
in the Method Editor:
|
Step
|
Action
|
|
1
|
Choose Edit:BufferPrep
Recipes.
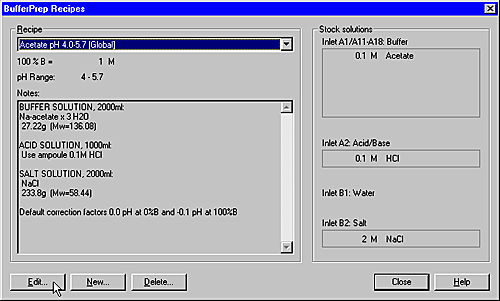
Result: The BufferPrep Recipes dialog box
opens.
The illustration below shows the BufferPrep
Recipes dialog box with a recipe selected:
|
|
2
|
Click the New button.
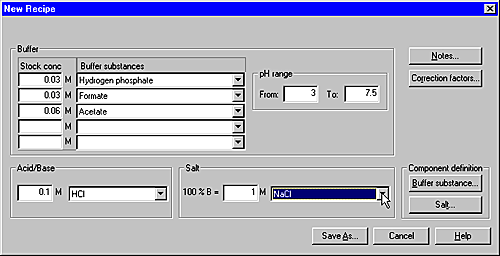
Result: The New Recipe dialog box opens.
The illustration below shows a complete example of a BufferPrep recipe in the New Recipe dialog box.
|
|
3
|
Select buffers from the Buffer
substances droplists and type stock concentrations in
the corresponding Stock conc box.
See “How to define a new buffer substance” below if the desired
substance is not available.
|
|
4
|
Select either HCl (acid)
or NaOH (base) from the Acid/Base droplist and type the
required stock concentration (typically 0.1 M)
|
|
5
|
Select a salt from the Salt droplist
and type the maximum outlet concentration of the salt for 100%B (typically 1.0 M).
See “How to define a new salt” below if the desired salt is
not available.
|
|
6
|
Type the desired pH range minimum and maximum values
in the From and To boxes.
See “How to select the pH range” below this table.
|
|
7
|
-
Click the Notes button (optional).
-
Type your notes about the recipe in the displayed
dialog box.
-
Click OK to
return to the New Recipe dialog
box.
|
|
8
|
Click Save as to
save the recipe under a new name.
Note: A warning
message will appear if any of the recipe values are unfeasible.
|
|
9
|
Result: The new
recipe is added to the recipe list.
|
Note: It is recommended
that restricted access be given to the right to edit global recipes.
The recipes are either globally available to all users, or
only personally available. It is best not to edit the globally available
recipes, unless you save the changes under a new recipe name, since
other users may not appreciate the changes.
|